1.使用线程池的好处
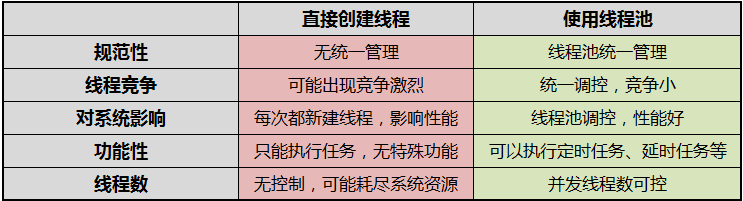
2.JUC中几种常用的线程池
java.util.concurrent包下的Executors工厂类,提供了一系列的线程池的创建方法,其构造方法如下:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, //线程池线程核心数量,线程池维护线程的最少数量
int maximumPoolSize, //线程池最大线程数量
long keepAliveTime, //空闲线程存活时间
TimeUnit unit, //存活时间的时间单位
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, //存储任务的线程队列
ThreadFactory threadFactory, //线程工厂
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) { //拒绝策略
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
其中常用的线程池有四种,分别是fixedThreadPool、cachedThreadPool、ScheduledThreadPool和SingleThreadExecutor。他们分别适用在不同的场合。
2.1 newFixedThreadPool
特点:
- 用于创建一个可重用、固定线程数量的线程池;
- 当线程池中线程都处于运行中时,新来的线程会进入等待状态,直到线程池中出现一个空闲线程;
- 当一个线程在任务中途退出、终止时,会有一个新的线程来替代它继续完成后面未完成的任务。
- 除非采用显式关闭的方法去关闭某个线程,否则线程会一直存在,不会释放资源。
- 任务存储在无界阻塞队列中
- 适用场景:长期任务
构造方法:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
实例代码:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import org.junit.Test;
public class ExecutorsTest extends Thread{
private int index;
public ExecutorsTest(int i)
{
this.index = i;
}
public void run()
{
try
{
System.out.println("[Thread"+this.index+"]" +"start..");
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*10000));
System.out.println("[Thread"+this.index+"]" + "end");
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
service.execute(new ExecutorsTest(i));
}
service.shutdown();
}
}
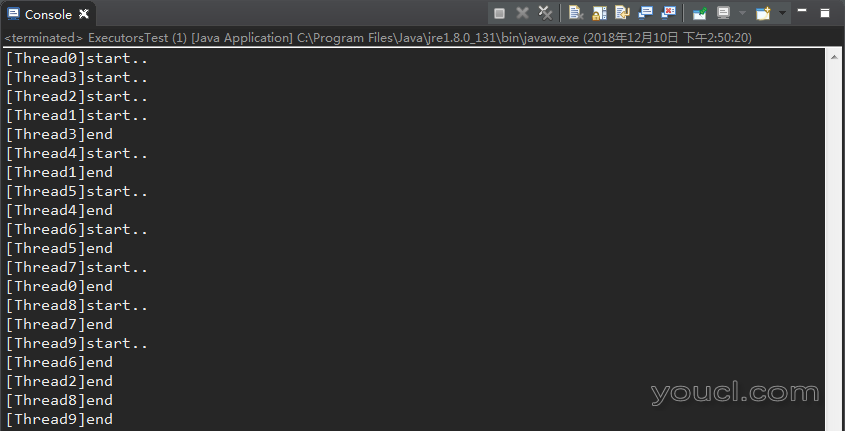
因为线程池中线程数量一共有4个,所以当一次有大于4个的任务需要执行时,因为线程池中无空闲线程,后续任务进入等待状态,当其他任务执行完毕后,线程空闲,则马上开始执行正在等待的任务。
2.1 newCachedThreadPool
特点:
- 线程池数量上限为:Integer.MaxValue(2147483647);
- 线程池默认空闲60S,超过60S会从线程池中移除;
- 新来任务时,先检查是否有空闲线程可使用,若无,则创建一个新线程执行任务;
- 任务存储在同步队列中。
- 适用场景:短时异步任务。
构造函数:
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
示例代码:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import org.junit.Test;
public class ExecutorsTest extends Thread{
private int index;
public ExecutorsTest(int i)
{
this.index = i;
}
public void run()
{
try
{
System.out.println("[Thread"+this.index+"]" +"start..");
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*1000));
System.out.println("[Thread"+this.index+"]" + "end");
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
service.execute(new ExecutorsTest(i));
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
service.execute(new ExecutorsTest(i));
}
service.shutdown();
}
}
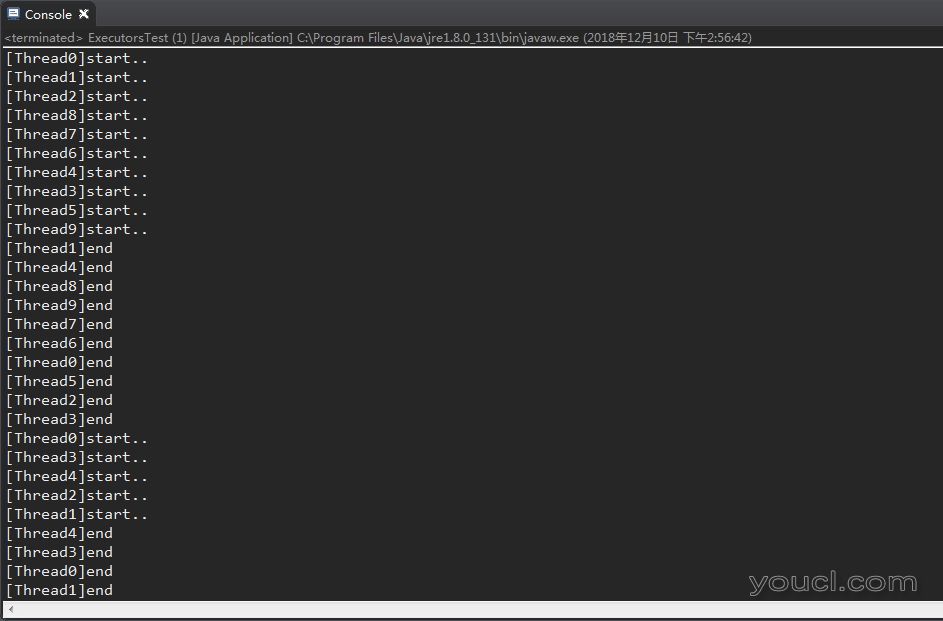
创建10个工作线程用于处理任务,当线程执行完毕后,处于空闲状态,此时若出现新的任务,则会从线程池中用空闲的线程来处理新的任务。若没有空闲线程,则开启新线程处理。
2.3 newSingleThreadExecutor
特点:
- 创建一个单个Worker的线程;
- 线程会按照顺序依次执行;
- 任务存储在无界阻塞队列中
- 适用场景:需要按照顺序执行的任务。
构造方法:
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
实例代码:
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import org.junit.Test;
public class ExecutorsTest extends Thread{
private int index;
public ExecutorsTest(int i)
{
this.index = i;
}
public void run()
{
try
{
System.out.println("[Thread"+this.index+"]" +"start..");
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*1000));
System.out.println("[Thread"+this.index+"]" + "end");
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
ExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
service.execute(new ExecutorsTest(i));
}
service.shutdown();
}
}
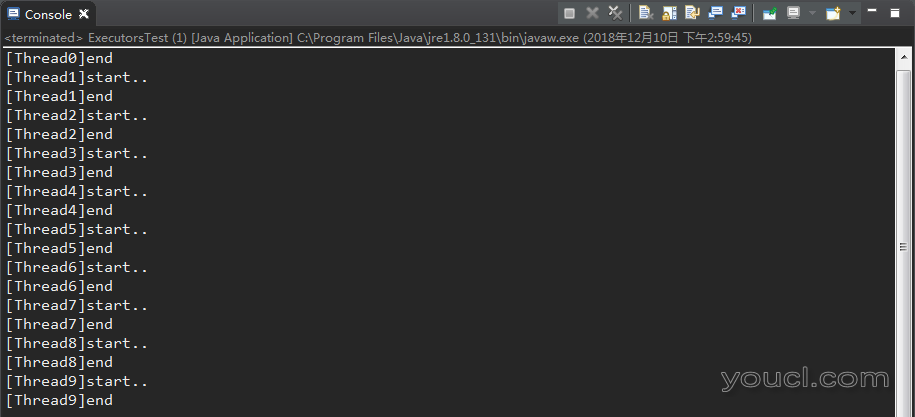
出现多个任务时,SingleThreadExecutor会按照顺序依次执行各个任务。
2.4 newScheduledThreadPool
特点:
- 任务存储在无界延迟队列中
- 适用场景:需要定期执行或延迟执行的任务
构造方法:
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
实例代码一(scheduleAtFixedRate的使用):
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ExecutorsTest2 extends Thread{
private int index;
public ExecutorsTest2()
{
}
public void run()
{
try
{
System.out.println("[Current Time is "+new Date().toString());
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
/*
* 执行定时任务newScheduledThreadPool
*/
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);
//5秒后开始执行,每隔一秒执行一次
service.scheduleAtFixedRate(new ExecutorsTest2(), 5, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
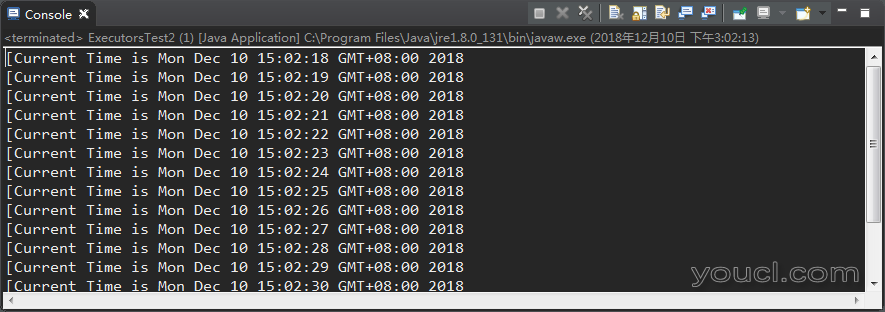
scheduleAtFixedRate方法,一共四个参数,分别是:需要执行的任务task、延迟执行时间t1、每次执行任务的时间间隔t2、时间间隔单位。 含义是:在t1时间过后,以 1次/t2 的频率来不断执行 task。 上述代码中,在5秒延迟后,以 1次/1秒的频率执行 打印当前时间的任务。
实例代码二(scheduleWithFixedDelay的使用):
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ExecutorsTest3 extends Thread{
private int index;
public ExecutorsTest3()
{
}
public void run()
{
try
{
//每次任务大约耗时1秒
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("[Current Time is "+new Date().toString());
}catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
/*
* 执行定时任务newScheduledThreadPool
*/
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);
//5秒后开始执行,每次任务执行完后延迟3秒后,继续执行下一次
service.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new ExecutorsTest3(), 5, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
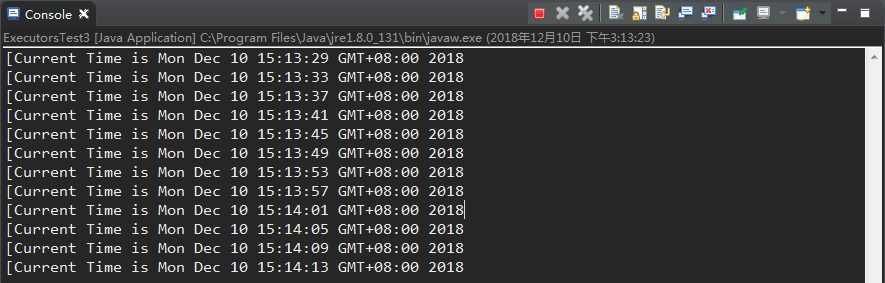
scheduleWithFixedDelay也是四个参数,分别是:待执行的任务Task,延迟时间t1,每次任务执行完毕后延迟t2秒后执行下次任务,延迟时间单位。








