软件存储库(简称“ repo ”)是用于保存和维护软件包的中央文件存储位置,用户可以从中检索软件包并在其计算机上安装。
存储库通常存储在网络上的服务器上,例如互联网,可由多个用户访问。 但是,您可以在计算机上创建和配置本地存储库,并将其作为单个用户访问,或允许访问LAN ( 局域网 )上的其他计算机。
设置本地存储库的一个优点是您不需要Internet连接来安装软件包。
YUM(Yellowdog Updater Modified)是一种广泛使用的基于Linux( RedHat Package Manager )Linux系统的软件包管理工具,可以在Red Hat / CentOS Linux上轻松安装软件。
在本文中,我们将解释如何在CentOS 7 VPS上通过HTTP ( Nginx )Web服务器设置本地YUM存储库,并向您展示如何在客户端CentOS 7计算机上查找和安装软件包。
我们的测试环境
Yum HTTP Repository Server: CentOS 7 [192.168.0.100] Client Machine: CentOS 7 [192.168.0.101]
第1步:安装Nginx Web服务器
1.首先使用YUM包管理器从EPEL存储库安装Nginx HTTP服务器,如下所示。
# yum install epel-release # yum install nginx
2.安装Nginx Web服务器后,您可以首次启动它并使其在系统引导时自动启动。
# systemctl start nginx # systemctl enable nginx # systemctl status nginx
3.接下来,您需要打开端口80和443以允许Web流量到Nginx服务,使用以下命令更新系统防火墙规则以允许HTTP和HTTPS上的入站数据包。
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=http # firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=https # firewall-cmd --reload
4.现在,您可以使用以下URL确认您的Nginx服务器已启动并正在运行; 如果您看到默认的Nginx网页,一切都很好。
http://SERVER_DOMAIN_NAME_OR_IP
Nginx默认页面
第2步:创建Yum本地存储库
5.在此步骤中,您需要安装所需的软件包以创建,配置和管理本地存储库。
# yum install createrepo yum-utils
6.接下来,创建将存储包和任何相关信息的必要目录(yum存储库)。
# mkdir -p /var/www/html/repos/{base,centosplus,extras,updates}
7.然后使用reposync工具将CentOS YUM存储库同步到本地目录,如图所示。
# reposync -g -l -d -m --repoid=base --newest-only --download-metadata --download_path=/var/www/html/repos/ # reposync -g -l -d -m --repoid=centosplus --newest-only --download-metadata --download_path=/var/www/html/repos/ # reposync -g -l -d -m --repoid=extras --newest-only --download-metadata --download_path=/var/www/html/repos/ # reposync -g -l -d -m --repoid=updates --newest-only --download-metadata --download_path=/var/www/html/repos/
样本输出
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.fibergrid.in * epel: mirror.xeonbd.com * extras: mirrors.fibergrid.in * updates: mirrors.fibergrid.in base/7/x86_64/group | 891 kB 00:00:02 No Presto metadata available for base (1/9911): 389-ds-base-snmp-1.3.7.5-18.el7.x86_64.rpm | 163 kB 00:00:02 (2/9911): 389-ds-base-devel-1.3.7.5-18.el7.x86_64.rpm | 267 kB 00:00:02 (3/9911): ElectricFence-2.2.2-39.el7.i686.rpm | 35 kB 00:00:00 (4/9911): ElectricFence-2.2.2-39.el7.x86_64.rpm | 35 kB 00:00:00 (5/9911): 389-ds-base-libs-1.3.7.5-18.el7.x86_64.rpm | 695 kB 00:00:04 (6/9911): GConf2-devel-3.2.6-8.el7.i686.rpm | 110 kB 00:00:00 (7/9911): GConf2-devel-3.2.6-8.el7.x86_64.rpm | 110 kB 00:00:00 (8/9911): GConf2-3.2.6-8.el7.i686.rpm | 1.0 MB 00:00:06
在上面的命令中,选项:
-
-g- 允许在下载后删除未通过GPG签名检查的软件包。 -
-l- 启用yum插件支持。 -
-d- 允许删除存储库中不再存在的本地软件包。 -
-m- 允许下载comps.xml文件。 -
--repoid- 指定存储库ID。 -
--newest-only---newest-only告知reposync仅在repos中提取每个包的最新版本。 -
--download-metadata- 允许下载所有非默认元数据。 -
--download_path- 指定下载包的路径。
8.接下来,检查本地目录的内容以确保所有程序包已在本地同步。
# ls -l /var/www/html/repos/base/ # ls -l /var/www/html/repos/base/Packages/ # ls -l /var/www/html/repos/centosplus/ # ls -l /var/www/html/repos/centosplus/Packages/ # ls -l /var/www/html/repos/extras/ # ls -l /var/www/html/repos/extras/Packages/ # ls -l /var/www/html/repos/updates/ # ls -l /var/www/html/repos/updates/Packages/
9.现在,通过运行以下命令为本地存储库创建新的repodata,其中标志-g用于使用指定的.xml文件更新软件包组信息。
# createrepo -g comps.xml /var/www/html/repos/base/ # createrepo -g comps.xml /var/www/html/repos/centosplus/ # createrepo -g comps.xml /var/www/html/repos/extras/ # createrepo -g comps.xml /var/www/html/repos/updates/
10.要通过Web浏览器查看其中的存储库和包,请创建一个Nginx服务器块,该块指向存储库的根目录,如图所示。
# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/repos.conf
添加以下配置文件repos.conf 。
server {
listen 80;
server_name repos.test.lab; #change test.lab to your real domain
root /var/www/html/repos;
location / {
index index.php index.html index.htm;
autoindex on; #enable listing of directory index
}
}
保存文件并关闭它。
11.然后重新启动Nginx服务器并使用以下URL从Web浏览器查看存储库。
http://repos.test.lab
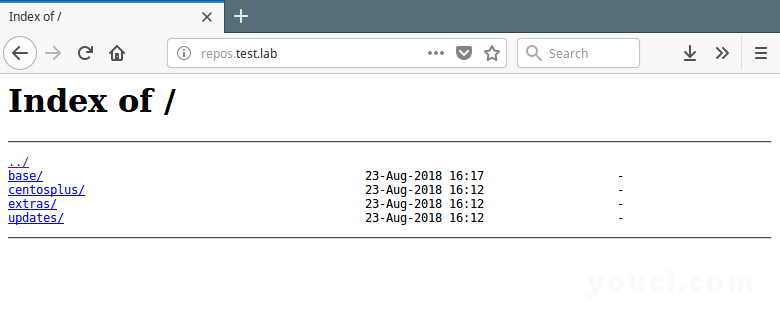
查看本地Yum存储库
第3步:创建Cron作业以同步和创建存储库
12.接下来,添加一个cron作业,该作业将自动将本地回购与官方CentOS回购同步,以获取更新和安全补丁。
# vim /etc/cron.daily/update-localrepos
在脚本中添加这些命令。
#!/bin/bash
##specify all local repositories in a single variable
LOCAL_REPOS=”base centosplus extras updates”
##a loop to update repos one at a time
for REPO in ${LOCAL_REPOS}; do
reposync -g -l -d -m --repoid=$REPO --newest-only --download-metadata --download_path=/var/www/html/repos/
createrepo -g comps.xml /var/www/html/repos/$REPO/
done
保存脚本并关闭它并在其上设置适当的权限。
# chmod 755 /etc/cron.daily/update-localrepos
第4步:在客户端计算机上设置本地Yum存储库
13.现在在CentOS客户端计算机上,将本地存储库添加到YUM配置中。
# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/local-repos.repo
将以下配置复制并粘贴到local-repos.repo文件中(必要时进行更改)。
[local-base] name=CentOS Base baseurl=http://repos.test.lab/base/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 [local-centosplus] name=CentOS CentOSPlus baseurl=http://repos.test.lab/centosplus/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 [local-extras] name=CentOS Extras baseurl=http://repos.test.lab/extras/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1 [local-updates] name=CentOS Updates baseurl=http://repos.test.lab/updates/ gpgcheck=0 enabled=1
保存文件并开始使用本地YUM镜像。
14.接下来,运行以下命令以在客户端计算机上的可用YUM存储库列表中查看本地存储库。
# yum repolist OR # yum repolist all
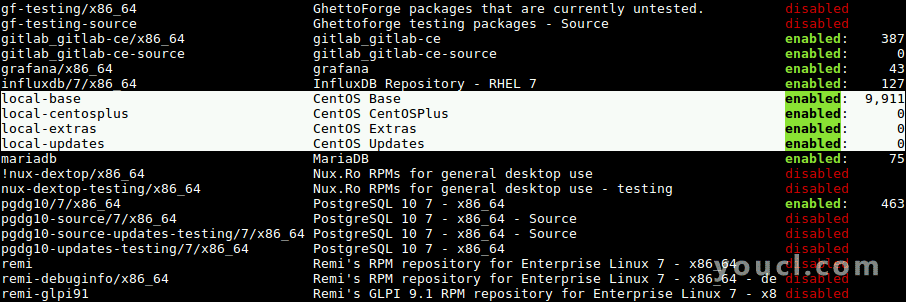
在客户端上查看本地Yum存储库
就这样! 在本文中,我们已经解释了如何在CentOS 7上设置本地YUM存储库。我们希望您发现本指南很有用。 如果您有任何问题或想要分享的任何其他想法,请使用下面的评论表。








