Linux正常运行时间命令为示例初学者解释
如果你是一个Linux新手,并且对系统管理感兴趣,或者你想成为一名高级用户,那么你需要对命令行有深入的了解。 有几个你应该知道的命令,其中一个是正常运行时间 。 在本文中,我们将使用一些易于理解的示例来讨论此命令的基础知识。
但在此之前,值得一提的是,本教程中使用的所有示例都已在Ubuntu 16.04机器上进行了测试。
Linux正常运行时间命令
顾名思义,正常运行时间命令会为您提供系统启动(或运行)的时间。 这是它的语法:
uptime [options]
下面是该工具的手册页解释它的方式:
uptime gives a one line display of the following information. The current time, how long the system
has been running, how many users are currently logged on, and the system load averages for the past
1, 5, and 15 minutes.
下面的问答样例应该能让你更好地了解正常运行时间命令的工作原理。
Q1。 如何使用正常运行时间命令
正常运行时间的基本使用非常简单 - 只需编写命令的名称,然后按回车即可。
uptime
这是工具产生的输出类型:

因此,第一个条目是当前时间,然后“上”显示系统正在运行,5:53是系统已经启动的总时间,最后是系统负载平均值。 以防万一你想知道更多,这里是正常运行时间手册页上最后一项说:
System load averages is the average number of processes that are either in a runnable or
uninterruptable state. A process in a runnable state is either using the CPU or waiting to use the
CPU. A process in uninterruptable state is waiting for some I/O access, eg waiting for disk.
The averages are taken over the three time intervals. Load averages are not normalized for the
number of CPUs in a system, so a load average of 1 means a single CPU system is loaded all the
time while on a 4 CPU system it means it was idle 75% of the time.
Q2。 如何使工具以相当的格式显示时间
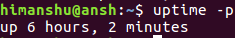
如果你只是想知道系统已经启动的时间,并且也是以一种更易读的格式,使用-p命令行选项。
uptime -p
下面是我们的例子中输出的命令:
Q3。 系统启动后,如何使运行时间显示日期/时间
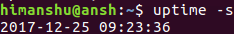
您也可以设定正常运行时间,特别是显示自系统运行以来的时间/日期。 这可以使用-s命令行选项完成。
uptime -s
下面是我们的例子中输出的命令:
Q4。 如何获取版本信息和一般帮助
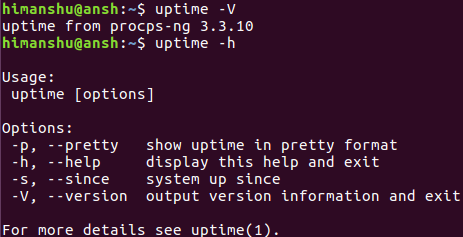
使用-V选项获取版本信息,使用-h获得一般帮助。
uptime -V
uptime -h
结论
正如您所看到的,正常运行时间命令很容易理解和使用。 它不提供许多功能(或命令行选项)。 这里提供了所有提供的内容。 所以只要练习这些选项,就可以在日常工作中使用正常运行了。 以防万一你需要,这里是该工具的手册页 。








