嗨! 我们已经涵盖了shell脚本的基础知识,例如接受输入,通过算术运算处理数据,并在本教程的前面部分( 第1 部分和第2部分 )中生成和显示输出。 在这部分中,我们将深入研究一个编程语言中更高级的主题 - 在程序中做出决定,但这次我们将使用bash shell来执行。 让我们开始吧!
介绍
我们今天的大多数编程语言都可以根据我们设定的条件做出决定。 条件是一个表达式,其计算结果为布尔值 - true或false。 任何程序员都可以根据他对他的程序的决定和逻辑,使他的程序变得聪明。 bash shell支持if和switch(case)决策语句。
如果声明
如果是允许程序员根据他指定的条件在程序中作出决定的声明。 如果满足条件,程序将执行某些代码行,否则程序将执行程序员指定的其他任务。 以下是bash shell中if语句支持的语法。
一般语法
单决:
if <condition>
then
### series of code goes here
fi
双重决定:
if <condition>
then
### series of code if the condition is satisfied
else
### series of code if the condition is not satisfied
fi
多个条件:
if <condition1>
then
### series of code for condition1
elif <condition2>
then
### series of code for condition2
else
### series of code if the condition is not satisfied
fi
单括号语法
if [ condition ]
then
### series of code goes here
fi
双括号语法
if ((condition))
then
### series of code goes here
fi
单括号语法是bash shell中最早支持的语法。 它与Linux中的所有条件语句一起使用。 同时,双括号语法用于基于数字的条件语句,以向程序员提供熟悉的语法。 所有类型的if语句都需要一个指定的条件才能执行一个任务。
Linux中的条件语句
条件语句与决策控制语句一起使用。 可以在bash shell中使用不同类型的条件语句,最常见的是:基于文件,基于字符串和基于算术的条件。
基于文件的条件
基于文件的条件是一元表达式,通常用于检查文件的状态。 以下列表显示了bash shell中最常用的基于文件的条件。
| 操作员 | 描述 |
| -一份文件 | 如果文件存在,则返回true |
| -b文件 | 如果文件存在且返回true,则为块特殊文件 |
| -c文件 | 如果文件存在并且是一个字符特殊文件,则返回true |
| -d文件 | 如果文件存在并且是目录,则返回true |
| -e文件 | 如果文件存在,则返回true |
| -r文件 | 如果文件存在且可读,则返回true |
| -s文件 | 如果文件存在并且其大小为零,则返回true |
| -s文件 | 如果文件存在并且其大小为零,则返回true |
| -w文件 | 如果文件存在且可写,则返回true |
| -x文件 | 如果文件存在且可执行,则返回true |
| -N文件 | 如果文件存在并且自上次读取以来已被修改,则返回true |
进行基于文件的决策
让我们举一个例子来说明如何在bash脚本中构建基于文件的决策。 在这个例子中,我们将创建一个脚本来确定文件是否存在于主目录中。
#!/bin/bash
cd
ls
if [ -e sample.sh ]
then
echo "file exists!"
else
echo "file does not exist"
fi
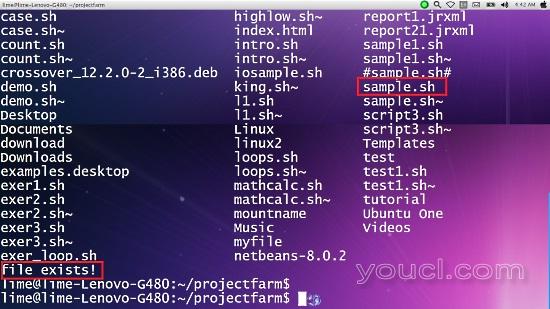
在这个例子中,我们确保shell将返回到主目录,而不管我们当前的活动目录使用cd命令。 此外, ls命令用于显示目录中的文件列表,以便我们验证文件是否真的存在。 您可以看到,脚本输出文本“文件存在!” 因为sample.sh在主目录中。
Note: The shell compiler is very strict in terms of syntax especially with spaces. There should be a space between if and the open bracket and in between brackets and the condition.
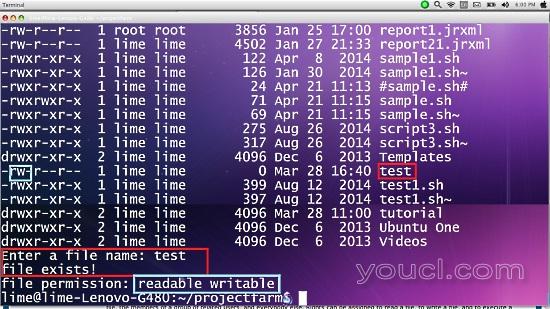
现在让我们通过让用户输入脚本名称并确定给定文件的权限,使我们的代码更加动态,从而改进我们的脚本。
#!/bin/bash
cd
ls -l
read -p "Enter a file name: " filename
if [ -e $filename ]
then
echo "file exists!"
if [ -r $filename ]
then
status="readable "
fi
if [ -w $filename ]
then
status=$status"writable "
fi
if [ -x $filename ]
then
status=$status"executable"
fi
echo "file permission: "$status
else
echo "file does not exist"
fi
基于字符串的条件
在bash shell中也可以根据字符串用户输入进行决策。 基于字符串的条件返回一个二进制表达式作为结果意义,如果指定的条件满足,则返回true,它返回false。 以下是常用的基于字符串的条件运算符:
| 操作员 | 描述 |
| == | 如果字符串相等则返回true |
| != | 如果字符串不相等,则返回true |
| -n | 如果要测试的字符串不为空,则返回true |
| -z | 如果要测试的字符串为空,则返回true |
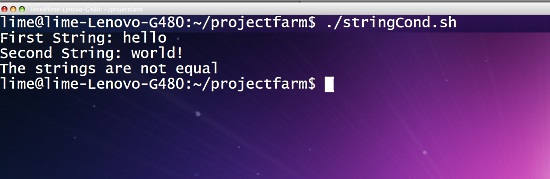
我们来创建一个使用基于字符串的条件语句的示例脚本。 脚本将允许用户输入两个字符串,并评估其中一个字符串是否为空,两个字符串相等且不相等。
#!/bin/bash
read -p "First String: " str1
read -p "Second String: " str2
if [ -z "$str1" ]
then
echo "The 1st string is null"
elif [ -z "$str2" ]
then
echo "The 2nd string is null"
else
if [ $str1 == $str2 ]
then
echo "The strings are equal"
else
echo "The strings are not equal"
fi
fi
基于算术的条件
shell提供了几种声明基于算术的条件的方法。 首先是使用可与旧式单括号语法一起使用的助记符,另一种是使用可与双括号一起使用的数学友好符号
以下是shell中基于算术的条件语句的可用助记符列表:
| 操作员 | 用法/说明 |
| -eq | 等于 |
| -ge | 大于或等于 |
| -gt | 比...更棒 |
| -le | 小于或等于 |
| -lt | 少于 |
| 一个 | 不平等 |
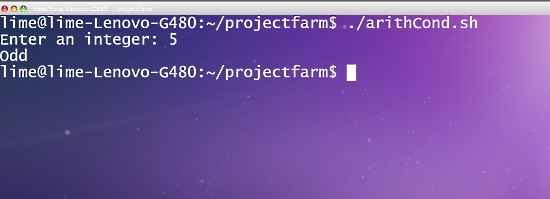
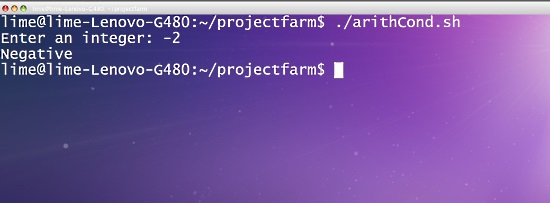
让我们创建一个接受用户整数的脚本,并确定整数是零,负数,奇数还是偶数。
#!/bin/bash
read -p "Enter an integer: " int1
if [ $int1 -eq 0 ]
then
echo "Zero"
elif [ $int1 -lt 0 ]
then
echo "Negative"
else
if [ $((int1%2)) -eq 0 ]
then
echo "Even"
else
echo "Odd"
fi
fi
双括号语法的算术运算符:
| 操作员 | 用法/说明 |
| == | 等于 |
| > = | 大于或等于 |
| > | 比...更棒 |
| <= | 小于或等于 |
| < | 少于 |
| != | 不平等 |
现在,我们来重构我们以前的脚本,并使用双括号语法:
#!/bin/bash
read -p "Enter an integer: " int1
if (( $int1 == 0 ))
then
echo "Zero"
elif (( $int1 < 0 ))
then
echo "Negative"
else
if (( $((int1%2)) == 0 ))
then
echo "Even"
else
echo "Odd"
fi
fi
切换语句
switch语句是shell脚本中的另一种条件语句。 它允许程序员以比较容易的方式比较几个值与变量相比,如果条件语句。 switch语句的语法是:
case in
<pattern1>)
##series of code for pattern1
;;
<pattern2>)
##series of code for pattern2
;;
<patternN>)
##series of code for patternN
;;
*)
##default statements
esac
该模式是变量的可能值。 每个图案都用一个双分号分隔,该分号用作模式的中断语句。 switch语句使用一个esac语句关闭。
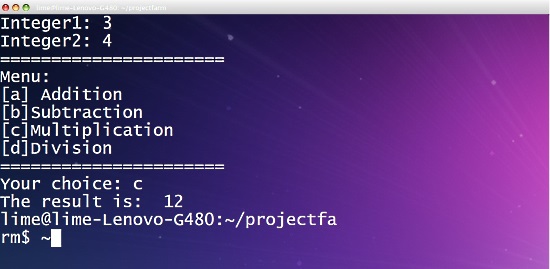
#!/bin/bash
clear
read -p "Integer1: " int1
read -p "Integer2: " int2
echo "======================"
printf "Menu: \n[a] Addition\n[b]Subtraction\n[c]Multiplication\n[d]Division\n"
echo "======================"
read -p "Your choice: " choice
res=0
case $choice in
a)
res=$((int1+int2))
;;
b)
res=$((int1-int2))
;;
c)
res=$((int1*int2))
;;
d)
res=$((int1/int2))
;;
*)
echo "Invalid input"
esac
echo "The result is: " $res
结论
bash shell为程序员提供了许多有用的工具。 就像现在的大多数编程语言一样,它也能够做出有条件的决策,使shell脚本更具互动性和智能性。 下一系列将重点介绍控制结构。 '直到下一次。
参考文献
- http://www.gnu.org/software/bash/manual/html_node/Bash-Conditional-Expressions.html
- https://linuxacademy.com/blog/linux/conditions-in-bash-scripting-if-statements/
下一课: 重复控制结构








