SpamAssassin-ClamAV-Procmail-Howto
版本1.0
作者:Falko Timme
本文档介绍了如何安装SpamAssassin(用于过滤SPAM)和ClamAV(用于过滤病毒,木马,蠕虫等)以及如何使用procmail配方来调用它们。 适用于Sendmail或Postfix向本地用户发送电子邮件的场景。 所有* nix操作系统都应该工作(或许有关于路径等的轻微变化)。 到目前为止,我已经在Debian Woody上测试过了。
最后,您将有一个系统,Sendmail或Postfix会向本地用户发送电子邮件; 电子邮件传递给procmail,它会调用SpamAssassin和ClamAV,以便在电子邮件到达用户收件箱之前过滤电子邮件。 但是,本文档中未介绍安装Sendmail和Postfix。
这是一个实践指南; 它不包括理论背景。 他们在网络上的许多其他文档中被处理。
本文档不附带任何形式的保证!
请注意:如果您使用服务器控制面板42go ISP-Manager,则无需遵循本教程,因为42go ISP-Manager附带SpamAssassin和ClamAV,并且可以通过42go ISP-Manager配置!
1安装SpamAssassin
有多种安装SpamAssassin的方法。 我会在这里描述三个:
| 1。 | 使用Perl Shell安装 以root身份登录到您的命令行,并运行以下命令启动Perl shell: perl -MCPAN -e shell 如果你第一次运行Perl shell,你会被问到一些问题。 在大多数情况下,默认答案都可以。 请注意:如果您在系统上运行防火墙,您可能必须在Perl shell上执行此操作,以便Perl shell能够在没有任何延迟的情况下获取所需的模块。 您可以打开它。 与这里描述的其他两种方法相比,Perl shell的最大优点是它在安装新模块时关心依赖关系。 也就是说,如果在安装另一个模块时Perl shell询问您是否应该为您安装必备模块,则会丢失必要的Perl模块。 你应该用“是”回答这个问题。 运行以下命令来安装SpamAssassin和其他一些所需的模块: 安装HTML :: Parser 如果您的系统上已经安装了一个模块,您将收到类似于此的消息: HTML :: Parser是最新的。 成功安装模块如下所示: / usr / bin / make install - 确定 |
| 2。 | 从源安装 ( 请注意:在从源文件编译SpamAssassin之前,必须先安装Perl模块(至少包含HTML :: Parser ),如果不是,请使用本文中描述的其他两种方法之一安装它们,或者获取源来自http://www.cpan.org并编译它们,这与SpamAssassin这里描述的步骤类似。) cd / tmp |
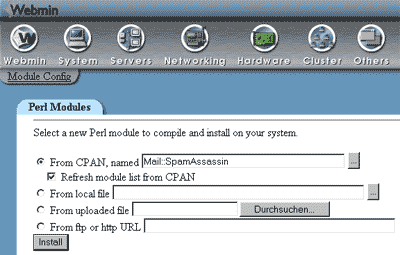
| 3。 | 使用Webmin进行安装 如果您的系统上安装了webmin( http://www.webmin.com ),您可以使用它来安装Perl模块。 登录到webmin,转到其他 - > Perl模块 ,并安装SpamAssassin:
如果您收到错误消息,这主要是由于系统中缺少一些必备模块。 安装它们(至少需要HTML :: Parser ),然后尝试再次安装要安装的模块。 |
SpamAssassin将安装到/ usr / local / share / spamassassin / 。
2安装ClamAV
cd / tmp
groupadd clamav
useradd -g clamav -s / bin / false -c“Clam AntiVirus”clamav
wget http://heanet.dl.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/clamav/clamav-0.67.tar.gz
tar xvfz clamav-0.67.tar.gz
cd clamav-0.67
./configure --sysconfdir = / etc
( 请注意: ./configure --help 提供了可用的所有配置选项的列表。)
使
su -c“make install”
如果你跑
蛤蜊
现在您将收到一条错误消息:
错误:请编辑示例配置文件/etc/clamav.conf。
您至少必须删除 Example 指令。 我的 /etc/clamav.conf 如下所示:
## ## Example config file for the Clam AV daemon ## Please read the clamav.conf(5) manual before editing this file. ## # Comment or remove the line below. #Example # Uncomment this option to enable logging. # LogFile must be writable for the user running the daemon. # Full path is required. #LogFile /tmp/clamd.log # By default the log file is locked for writing - the lock protects against # running clamd multiple times (if want to run another clamd, please # copy the configuration file, change the LogFile variable, and run # the daemon with --config-file option). That's why you shouldn't uncomment # this option. #LogFileUnlock # Maximal size of the log file. Default is 1 Mb. # Value of 0 disables the limit. # You may use 'M' or 'm' for megabytes (1M = 1m = 1048576 bytes) # and 'K' or 'k' for kilobytes (1K = 1k = 1024 bytes). To specify the size # in bytes just don't use modifiers. #LogFileMaxSize 2M # Log time with an each message. #LogTime # Use system logger (can work together with LogFile). #LogSyslog # Enable verbose logging. #LogVerbose # This option allows you to save the process identifier of the listening # daemon (main thread). #PidFile /var/run/clamd.pid # Path to a directory containing .db files. # Default is the hardcoded directory (mostly /usr/local/share/clamav, # it depends on installation options). #DatabaseDirectory /var/lib/clamav # The daemon works in local or network mode. Currently the local mode is # recommended for security reasons. # Path to the local socket. The daemon doesn't change the mode of the # created file (portability reasons). You may want to create it in a directory # which is only accessible for a user running daemon. LocalSocket /tmp/clamd # Remove stale socket after unclean shutdown. #FixStaleSocket # TCP port address. #TCPSocket 3310 # TCP address. # By default we bind to INADDR_ANY, probably not wise. # Enable the following to provide some degree of protection # from the outside world. #TCPAddr 127.0.0.1 # Maximum length the queue of pending connections may grow to. # Default is 15. #MaxConnectionQueueLength 30 # When activated, input stream (see STREAM command) will be saved to disk before # scanning - this allows scanning within archives. #StreamSaveToDisk # Close the connection if this limit is exceeded. #StreamMaxLength 10M # Maximal number of a threads running at the same time. # Default is 5, and it should be sufficient for a typical workstation. # You may need to increase threads number for a server machine. #MaxThreads 10 # Thread (scanner - single task) will be stopped after this time (seconds). # Default is 180. Value of 0 disables the timeout. SECURITY HINT: Increase the # timeout instead of disabling it. #ThreadTimeout 500 # Maximal depth the directories are scanned at. MaxDirectoryRecursion 15 # Follow a directory symlinks. # SECURITY HINT: You should have enabled directory recursion limit to # avoid potential problems. #FollowDirectorySymlinks # Follow regular file symlinks. #FollowFileSymlinks # Do internal checks (eg. check the integrity of the database structures) # By default clamd checks itself every 3600 seconds (1 hour). #SelfCheck 600 # Execute a command when virus is found. In the command string %v and %f will # be replaced by the virus name and the infected file name respectively. # # SECURITY WARNING: Make sure the virus event command cannot be exploited, # eg. by using some special file name when %f is used. # Always use a full path to the command. # Never delete/move files with this directive ! #VirusEvent /usr/local/bin/send_sms 123456789 "VIRUS ALERT: %f: %v" # Run as selected user (clamd must be started by root). # By default it doesn't drop privileges. User clamav # Initialize the supplementary group access (for all groups in /etc/group # user is added in. clamd must be started by root). #AllowSupplementaryGroups # Don't fork into background. Useful in debugging. #Foreground # Enable debug messages in libclamav. #Debug ## ## Mail support ## # Uncomment this option if you are planning to scan mail files. ScanMail ## ## Archive support ## # Comment this line to disable scanning of the archives. ScanArchive # By default the built-in RAR unpacker is disabled by default because the code # terribly leaks, however it's probably a good idea to enable it. #ScanRAR # Options below protect your system against Denial of Service attacks # with archive bombs. # Files in archives larger than this limit won't be scanned. # Value of 0 disables the limit. # WARNING: Due to the unrarlib implementation, whole files (one by one) in RAR # archives are decompressed to the memory. That's why never disable # this limit (but you may increase it of course!) ArchiveMaxFileSize 10M # Archives are scanned recursively - e.g. if Zip archive contains RAR file, # the RAR file will be decompressed, too (but only if recursion limit is set # at least to 1). With this option you may set the recursion level. # Value of 0 disables the limit. ArchiveMaxRecursion 5 # Number of files to be scanned within archive. # Value of 0 disables the limit. ArchiveMaxFiles 1000 # Use slower decompression algorithm which uses less memory. This option # affects bzip2 decompressor only. #ArchiveLimitMemoryUsage ## ## Clamuko settings ## WARNING: This is experimental software. It is very likely it will hang ## up your system !!! ## # Enable Clamuko. Dazuko (/dev/dazuko) must be configured and running. #ClamukoScanOnLine # Set access mask for Clamuko. ClamukoScanOnOpen ClamukoScanOnClose ClamukoScanOnExec # Set the include paths (all files in them will be scanned). You can have # multiple ClamukoIncludePath options, but each directory must be added # in a seperate option. All subdirectories are scanned, too. ClamukoIncludePath /home #ClamukoIncludePath /students # Set the exclude paths. All subdirectories are also excluded. #ClamukoExcludePath /home/guru # Limit the file size to be scanned (probably you don't want to scan your movie # files ;)) # Value of 0 disables the limit. 1 Mb should be fine. ClamukoMaxFileSize 1M # Enable archive support. It uses the limits from clamd section. # (This option doesn't depend on ScanArchive, you can have archive support # in clamd disabled). # ClamukoScanArchive |
现在我们必须为ClamAV( /etc/init.d/clamd )创建一个init脚本:
#!/bin/bash
TMPDIR=/tmp
PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/X11R6/bin
case "$1" in
start)
echo "Starting ClamAV..."
if [ -S /tmp/clamd ]; then
echo "ClamAV is already running!"
else
/usr/local/bin/freshclam -d -c 10 --datadir=/usr/local/share/clamav
/usr/local/sbin/clamd
fi
echo "ClamAV is now up and running!"
;;
stop)
echo "Shutting down ClamAV..."
array=(`ps ax | grep -iw '/usr/local/bin/freshclam' | grep -iv 'grep' \
| awk '{print $1}' | cut -f1 -d/ | tr '\n' ' '`)
element_count=${#array[@]}
index=0
while [ "$index" -lt "$element_count" ]
do
kill -9 ${array[$index]}
let "index = $index + 1"
done
array=(`ps ax | grep -iw '/usr/local/sbin/clamd' | grep -iv 'grep' \
| awk '{print $1}' | cut -f1 -d/ | tr '\n' ' '`)
element_count=${#array[@]}
index=0
while [ "$index" -lt "$element_count" ]
do
kill -9 ${array[$index]}
let "index = $index + 1"
done
if [ -S /tmp/clamd ]; then
rm -f /tmp/clamd
fi
echo "ClamAV stopped!"
;;
restart)
$0 stop && sleep 3
$0 start
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart}"
exit 1
esac
exit 0
|
chmod 755 /etc/init.d/clamd
现在我们开始ClamAV:
/etc/init.d/clamd start
如果你跑
ps辅助
您现在将注意到一些 clamd 进程(使用socket / tmp / clamd )和一个 新鲜的 进程,负责获取最新的病毒库更新。 它们位于 / usr / local / share / clamav下 。 命令
/ usr / local / bin / freshclam -d -c 10 --datadir = / usr / local / share / clamav
在我们的clamd init脚本中,确保新鲜卡片每天检查10次新签名。
为了在启动时启动ClamAV ,请执行以下操作:
ln -s /etc/init.d/clamd /etc/rc2.d/S20clamd
ln -s /etc/init.d/clamd /etc/rc3.d/S20clamd
ln -s /etc/init.d/clamd /etc/rc4.d/S20clamd
ln -s /etc/init.d/clamd /etc/rc5.d/S20clamd
ln -s /etc/init.d/clamd /etc/rc0.d/K20clamd
ln -s /etc/init.d/clamd /etc/rc1.d/K20clamd
ln -s /etc/init.d/clamd /etc/rc6.d/K20clamd
3安装垃圾箱
trashscan 是一个shell脚本,它使procmail和ClamAV之间的连接(即,当一个电子邮件到达时, procmail被调用,其本身调用垃圾邮件,以使邮件扫描由ClamAV进行病毒)。 它与ClamAV一起。
cd /tmp/clamav-0.67/contrib/trashscan
tar xvfz trashscan-0.08.tar.gz
cd trashscan-0.08
cp -pf trashscan / usr / local / sbin /
现在我们必须在/ usr / local / sbin / trashscan的“Settinx”部分中调整一些变量 。 我的设置如下:
#!/bin/bash
#
# TrashScan v0.08; Scan email for viruses
# ZapCoded by Trashware; 13.10.2002
# Email: trashware@gmx.de
# Web: http://trashware.mirrorz.com
#
PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin
# --------------------------------------- Begin Settinx ---------------------------------------- #
SCANDIR=$HOME/tmp # Temp directory for virus scans.
# Security: Don't define public
# accessible directories here !!!
# $HOME/tmp should be fine.
#DECODER=metamail # Decoder: "metamail" or "uudeview"
#DECODPRG=metamail # Absolute path to decoder: metamail
DECODER=uudeview # Decoder: "metamail" or "uudeview"
DECODPRG=/usr/local/bin/uudeview # Absolute path to decoder: uudeview
VSCANPRG=/usr/local/bin/clamscan # Absolute path to the virus scanner
VSCANOPT="--quiet --tempdir=$HOME/tmp --recursive --max-files=500 \
--max-space=30M --unzip=/usr/bin/unzip --unrar=/usr/bin/unrar \
--unarj=/usr/bin/unarj --zoo=/usr/bin/zoo --lha=/usr/bin/lha \
--jar=/usr/bin/unzip --tar=/bin/tar --tgz=/bin/tar" # Parameters for the virus scanner.
# Security: Don't choose public
# accessible directories for the
# --tempdir definition !!!
# --tempdir=$HOME/tmp should be fine.
VSCANVEX=1 # Exitcode of the virus scanner if a
# virus was found
VSCANSUSP=mail.virus # File to store suspicious mail (see
# procmail.trashscan)
FORMAIL=formail # Absolute path to formail
PROCMAIL=procmail # Absolute path to procmail
SENDMAIL=sendmail # Absolute path to sendmail
CAT=cat # Absolute path to cat
GREP=grep # Absolute path to grep
LOGGER=logger # Absolute path to logger
LOGPRIO=mail.warn # Log level for logger
MKDIR=mkdir # Absolute path to mkdir
RM=rm # Absolute path to rm
SED=sed # Absolute path to sed
ALERTRCVR=virusadmin@example.com # Receiver of virus alert messages
ALERTSNDR=virusadmin@example.com # Sender of virus alert messages
ALERTCTCT=virusadmin@example.com # Person to contact (appears in the
# mail body of the virus alert)
# ---------------------------------------- End Settinx ---------------------------------------- #
|
请注意,我在脚本开头设置PATH变量:
PATH = / sbin:/ usr / sbin:/ bin:/ usr / bin:/ usr / local / bin:/ usr / local / sbin
这样我就不需要指定trashscan (例如formail , procmail , sendmail )所需的绝大多数程序,只要它们在PATH中 。
VSCANOPT指定了以各种压缩格式解压缩文件所需的某些程序的路径(如果电子邮件附带压缩的附件,例如zip,tar.gz)。 您不需要所有程序,但我建议您至少解压缩和安装tar (如果没有,请使用http://www.rpmfind.net搜索解压缩和tar,如果您使用基于rpm的分发,并安装相应的软件包
rpm -ivh的package.rpm
如果您使用Debian,您所要做的就是
apt-get install unzip tar
)。
请确保在发现病毒时指定收到通知的人的正确电子邮件地址。
4安装uudeview
trashscan 需要一个程序来解码电子邮件。 在上面的垃圾邮件设置中,我指定了trashscan应该使用我们现在将安装的uudeview 。
cd / tmp
wget http://www.fpx.de/fp/Software/UUDeview/download/uudeview-0.5.19.tar.gz
tar xvfz uudeview-0.5.19.tar.gz
cd uudeview-0.5.19
。/配置
使
安装
5配置Procmail
默认情况下, procmail 通常安装在大多数发行版上,所以我不会 在这里 安装 procmail 安装。 跑
哪个procmail
找出你的procmail的位置(在我的例子中是/ usr / bin / procmail )。
现在我将介绍如何为/ home / www / web1 / user / testuser下的homedir用户testuser配置procmail 。 确保此路径( / home , / home / www , / home / www / web1 , / home / www / web1 / user , / home / www / web1 / user / testuser )中的目录不是group-或世界可写。 他们应该有权限rwxr-xr-x (或755 )。 否则procmail可以拒绝正常工作!
首先,我们必须创建/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.forward文件,以便当testuser的邮件到达时, procmail将被调用。 它有以下内容:
"|/usr/bin/procmail -f-" |
chown testuser /home/www/web1/user/testuser/.forward
chmod 600 /home/www/web1/user/testuser/.forward
现在我们创建文件/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.procmailrc 。 这是procmail将寻找Recipe(即命令运行)的文件。 为了清楚的原因,我们只需在这个文件中包括我们的主菜谱:
## MAILDIR=$HOME/Maildir/ ## DEFAULT=$MAILDIR INCLUDERC=/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.antivirus.rc INCLUDERC=/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.html-trap.rc INCLUDERC=/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.spamassassin.rc |
( 请注意:如果您使用Maildir作为电子邮件, 请取消注释前两行,即,您的电子邮件存储在/ home / www / web1 / user / testuser / Maildir /而不是/ var / spool / mail下 )。
我们的第一个Recipe是/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.antivirus.rc :
# # procmail configuration for TrashScan: ZapCoded by Trashware; 13.10.2002 # # [ ... ] # ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- # # Virus scan section ... # # ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- # # 1. Run TrashScan :0 * multipart * !^X-Virus-Scan: | /usr/local/sbin/trashscan # 2. Filter tagged virus mails :0: * ^X-Virus-Scan: Suspicious /dev/null |
/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.html-trap.rc在下面讨论,所以我们的第二个配方是/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.spamassassin.rc :
# SpamAssassin sample procmailrc
#
# Pipe the mail through spamassassin (replace 'spamassassin' with 'spamc'
# if you use the spamc/spamd combination)
# The condition line ensures that only messages smaller than 250 kB
# (250 * 1024 = 256000 bytes) are processed by SpamAssassin. Most spam
# isn't bigger than a few k and working with big messages can bring
# SpamAssassin to its knees.
:0fw
* < 256000
| /usr/local/bin/spamassassin --prefs-file=/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.user_prefs
# All mail tagged as spam (eg. with a score higher than the set threshold)
# is moved to "/dev/null".
#:0:
#* ^X-Spam-Status: Yes
#/dev/null
# Work around procmail bug: any output on stderr will cause the "F" in "From"
# to be dropped. This will re-add it.
:0
* ^^rom[ ]
{
LOG="*** Dropped F off From_ header! Fixing up. "
:0 fhw
| sed -e '1s/^/F/'
}
|
这将导致所有电子邮件都被接受,即使是垃圾邮件(这将被标记为垃圾邮件,可以由用户的电子邮件客户端进行整理)。 此策略在第一阶段被推荐,直到您确定SpamAssassin正确识别您的电子邮件为止。 如果你想删除垃圾邮件,请改用这个.spamassassin.rc :
# SpamAssassin sample procmailrc
#
# Pipe the mail through spamassassin (replace 'spamassassin' with 'spamc'
# if you use the spamc/spamd combination)
# The condition line ensures that only messages smaller than 250 kB
# (250 * 1024 = 256000 bytes) are processed by SpamAssassin. Most spam
# isn't bigger than a few k and working with big messages can bring
# SpamAssassin to its knees.
:0fw
* < 256000
| /usr/local/bin/spamassassin --prefs-file=/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.user_prefs
# All mail tagged as spam (eg. with a score higher than the set threshold)
# is moved to "/dev/null".
:0:
* ^X-Spam-Status: Yes
/dev/null
# Work around procmail bug: any output on stderr will cause the "F" in "From"
# to be dropped. This will re-add it.
:0
* ^^rom[ ]
{
LOG="*** Dropped F off From_ header! Fixing up. "
:0 fhw
| sed -e '1s/^/F/'
}
|
接下来我们创建一个文件/home/www/web1/user/testuser/.user_prefs ,它将包含testuser的SpamAssassin设置:
# SpamAssassin user preferences file. See 'perldoc Mail::SpamAssassin::Conf' # for details of what can be tweaked. #* #* Note: this file is not read by SpamAssassin until copied into the user #* directory. At runtime, if a user has no preferences in their home directory #* already, it will be copied for them, allowing them to perform personalised #* customisation. If you want to make changes to the site-wide defaults, #* create a file in /etc/spamassassin or /etc/mail/spamassassin instead. ########################################################################### # How many hits before a mail is considered spam. required_hits 5.0 rewrite_subject 1 subject_tag ***SPAM*** |
SpamAssassin在每个电子邮件中运行一些测试,以确定它是否是垃圾邮件。 每个测试分配给该电子邮件的一定数量(如果测试是肯定的)。 积分将被添加。 required_hits是电子邮件被认为是垃圾邮件的点数。 5.0开始是一个合理的价值。
如果rewrite_subject为1,如果电子邮件被认为是垃圾邮件,电子邮件的主题将被标记为subject_tag,以便如果上述选择了适当的.spamassassin.rc ,则可以通过testuser的电子邮件客户端对邮件进行排序。
6配置电子邮件消毒剂
电子邮件消毒剂( http://www.impsec.org/email-tools/procmail-security.html )是一组procmail配方,形成一种内容过滤器。 例如,它可以禁用HTML电子邮件中的恶意JavaScript代码,并重命名可疑附件(例如example.exe被重命名为example.12345DEFANGED-exe,以便在Windows下只能通过简单的双击打开它,必须保存到磁盘首先被自动重命名,所以收件人被迫考虑是否打开附件。
cd / tmp
wget http://www.impsec.org/email-tools/html-trap.procmail.gz
gunzip html-trap.procmail.gz
echo'PATH =“/ usr / bin:$ PATH:/ usr / local / bin”'> /home/www/web1/user/testuser/.html-trap.rc
echo'SHELL = / bin / sh'>> /home/www/web1/user/testuser/.html-trap.rc
cat html-trap.procmail >> /home/www/web1/user/testuser/.html-trap.rc
7测试您的配置
您现在可以通过发送.exe附件,样本SPAM和示例病毒(如果有的话)来测试您的配置。
看看收到的邮件的标题。 它应该包含以下行:
X-Security:在server1.example.com上清理的MIME头信息请参见http://www.impsec.org/email-tools/sanitizer-intro.html了解详细信息。 $修订:1.140 $日期:2004-02-11 20:47:43-08
X-Virus-Scan:由server1.example.com上运行的TrashScan v0.08扫描
X-Spam-Checker-Version:SpamAssassin 2.63(2004-01-11)on server1.example.com
链接
SpamAssassin: http : //www.spamassassin.org/
ClamAV: http : //www.clamav.net/
Procmail: http : //www.procmail.org/
电子邮件消毒剂: http : //www.impsec.org/email-tools/procmail-security.html