本教程的先前版本由finid编写。
介绍
Docker是一个简化容器中应用程序进程管理过程的应用程序。 容器允许您在资源隔离的进程中运行应用程序。 它们与虚拟机类似,但容器更便携,更加资源友好,并且更依赖于主机操作系统。
有关Docker容器的不同组件的详细介绍,请查看Docker Ecosystem:Common Components to Introduction 。
在本教程中,您将在Debian 9上安装和使用Docker Community Edition(CE)。您将安装Docker本身,使用容器和映像,并将映像推送到Docker存储库。
先决条件
要学习本教程,您需要具备以下条件:
- 一个Debian 9服务器按照Debian 9初始服务器设置指南设置 ,包括一个sudo非root用户和一个防火墙。
- 如果您希望创建自己的图像并将其推送到Docker Hub,则可以使用Docker Hub上的帐户,如第7步和8所示。
第1步 - 安装Docker
官方Debian存储库中提供的Docker安装包可能不是最新版本。 为了确保我们获得最新版本,我们将从官方Docker存储库安装Docker。 为此,我们将添加一个新的包源,从Docker添加GPG密钥以确保下载有效,然后安装该包。
首先,更新现有的包列表:
sudo apt update
接下来,安装一些必备软件包,这些软件包允许通过HTTPS使用软件包:
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg2 software-properties-common
然后将官方Docker存储库的GPG密钥添加到您的系统:
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
将Docker存储库添加到APT源:
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
接下来,使用新添加的repo中的Docker包更新包数据库:
sudo apt update
确保您要从Docker repo而不是默认的Debian repo安装:
apt-cache policy docker-ce
虽然Docker的版本号可能不同,但您会看到这样的输出:
docker-ce:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 18.06.1~ce~3-0~debian
Version table:
18.06.1~ce~3-0~debian 500
500 https://download.docker.com/linux/debian stretch/stable amd64 Packages
请注意,未安装docker-ce ,但安装的候选者来自Debian 9的Docker存储库( stretch )。
最后,安装Docker:
sudo apt install docker-ce
现在应该安装Docker,守护进程启动,并启用进程启动进程。 检查它是否正在运行:
sudo systemctl status docker
输出应类似于以下内容,表明该服务处于活动状态并正在运行:
Output● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2018-07-05 15:08:39 UTC; 2min 55s ago
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 21319 (dockerd)
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
├─21319 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd://
└─21326 docker-containerd --config /var/run/docker/containerd/containerd.toml
现在安装Docker不仅可以提供Docker服务(守护程序),还可以使用docker命令行实用程序或Docker客户端。 我们将在本教程后面探讨如何使用docker命令。
第2步 - 在没有Sudo的情况下执行Docker命令(可选)
默认情况下, docker命令只能运行root用户或docker组中的用户,这是在Docker安装过程中自动创建的。 如果您尝试运行docker命令而不使用sudo作为前缀或不在docker组中,那么您将获得如下输出:
Outputdocker: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon. Is the docker daemon running on this host?.
See 'docker run --help'.
如果您想在运行docker命令时避免键入sudo ,请将您的用户名添加到docker组:
sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}
要应用新的组成员身份,请注销服务器并重新登录,或键入以下内容:
su - ${USER}
系统将提示您输入用户密码以继续。
通过键入以下内容确认您的用户现已添加到docker组:
id -nG
Outputsammy sudo docker
如果您需要将用户添加到您未登录的docker组,请使用以下命令明确声明该用户名:
sudo usermod -aG docker username
本文的其余部分假定您以docker组中的用户身份运行docker命令。 如果你选择不这样做,请在sudo加上命令。
让我们接下来探讨一下docker命令。
第3步 - 使用Docker命令
使用docker包括传递一系列选项和命令,后跟参数。 语法采用以下形式:
docker [option] [command] [arguments]
要查看所有可用的子命令,请键入:
docker
从Docker 18开始,可用子命令的完整列表包括:
Output
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
exec Run a command in a running container
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
images List images
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
info Display system-wide information
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
login Log in to a Docker registry
logout Log out from a Docker registry
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
ps List containers
pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry
push Push an image or a repository to a registry
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
run Run a command in a new container
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
search Search the Docker Hub for images
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
version Show the Docker version information
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
要查看特定命令可用的选项,请键入:
docker docker-subcommand --help
要查看有关Docker的系统范围信息,请使用:
docker info
让我们探讨其中的一些命令。 我们将从处理图像开始。
第4步 - 使用Docker镜像
Docker容器是从Docker镜像构建的。 默认情况下,Docker从Docker Hub中获取这些映像, Docker Hub是由Docker管理的Docker注册表,Docker项目背后的公司。 任何人都可以在Docker Hub上托管他们的Docker镜像,因此您需要的大多数应用程序和Linux发行版都将在那里托管图像。
要检查您是否可以从Docker Hub访问和下载图像,请键入:
docker run hello-world
输出将指示Docker正常工作:
OutputUnable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
9db2ca6ccae0: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:4b8ff392a12ed9ea17784bd3c9a8b1fa3299cac44aca35a85c90c5e3c7afacdc
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
...
Docker最初无法在本地找到hello-world图像,因此它从Docker Hub下载了图像,这是默认的存储库。 下载映像后,Docker从映像创建了一个容器,并在容器中执行了应用程序,显示了该消息。
您可以使用带有search子命令的docker命令search Docker Hub上可用的图像。 例如,要搜索Ubuntu映像,请键入:
docker search ubuntu
该脚本将对Docker Hub进行爬网,并返回名称与搜索字符串匹配的所有图像的列表。 在这种情况下,输出将类似于:
OutputNAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED
ubuntu Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux operating sys… 8320 [OK]
dorowu/ubuntu-desktop-lxde-vnc Ubuntu with openssh-server and NoVNC 214 [OK]
rastasheep/ubuntu-sshd Dockerized SSH service, built on top of offi… 170 [OK]
consol/ubuntu-xfce-vnc Ubuntu container with "headless" VNC session… 128 [OK]
ansible/ubuntu14.04-ansible Ubuntu 14.04 LTS with ansible 95 [OK]
ubuntu-upstart Upstart is an event-based replacement for th… 88 [OK]
neurodebian NeuroDebian provides neuroscience research s… 53 [OK]
1and1internet/ubuntu-16-nginx-php-phpmyadmin-mysql-5 ubuntu-16-nginx-php-phpmyadmin-mysql-5 43 [OK]
ubuntu-debootstrap debootstrap --variant=minbase --components=m… 39 [OK]
nuagebec/ubuntu Simple always updated Ubuntu docker images w… 23 [OK]
tutum/ubuntu Simple Ubuntu docker images with SSH access 18
i386/ubuntu Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux operating sys… 13
1and1internet/ubuntu-16-apache-php-7.0 ubuntu-16-apache-php-7.0 12 [OK]
ppc64le/ubuntu Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux operating sys… 12
eclipse/ubuntu_jdk8 Ubuntu, JDK8, Maven 3, git, curl, nmap, mc, … 6 [OK]
darksheer/ubuntu Base Ubuntu Image -- Updated hourly 4 [OK]
codenvy/ubuntu_jdk8 Ubuntu, JDK8, Maven 3, git, curl, nmap, mc, … 4 [OK]
1and1internet/ubuntu-16-nginx-php-5.6-wordpress-4 ubuntu-16-nginx-php-5.6-wordpress-4 3 [OK]
pivotaldata/ubuntu A quick freshening-up of the base Ubuntu doc… 2
1and1internet/ubuntu-16-sshd ubuntu-16-sshd 1 [OK]
ossobv/ubuntu Custom ubuntu image from scratch (based on o… 0
smartentry/ubuntu ubuntu with smartentry 0 [OK]
1and1internet/ubuntu-16-healthcheck ubuntu-16-healthcheck 0 [OK]
pivotaldata/ubuntu-gpdb-dev Ubuntu images for GPDB development 0
paasmule/bosh-tools-ubuntu Ubuntu based bosh-cli 0 [OK]
...
在OFFICIAL列中, OK表示由项目后面的公司构建和支持的图像。 一旦确定了要使用的图像,就可以使用pull子命令将其下载到计算机中。
执行以下命令将官方ubuntu映像下载到您的计算机:
docker pull ubuntu
您将看到以下输出:
OutputUsing default tag: latest
latest: Pulling from library/ubuntu
6b98dfc16071: Pull complete
4001a1209541: Pull complete
6319fc68c576: Pull complete
b24603670dc3: Pull complete
97f170c87c6f: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:5f4bdc3467537cbbe563e80db2c3ec95d548a9145d64453b06939c4592d67b6d
Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:latest
下载映像后,可以使用带有run子命令的下载映像运行容器。 正如您在hello-world示例中看到的,如果使用run子命令执行docker时尚未下载映像,则Docker客户端将首先下载映像,然后使用它运行容器。
要查看已下载到计算机的图像,请键入:
docker images
输出应类似于以下内容:
OutputREPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
ubuntu latest 16508e5c265d 13 days ago 84.1MB
hello-world latest 2cb0d9787c4d 7 weeks ago 1.85kB
正如您将在本教程后面看到的那样,用于运行容器的图像可以被修改并用于生成新图像,然后可以将其上载( 推送是技术术语)到Docker Hub或其他Docker注册表。
我们来看看如何更详细地运行容器。
第5步 - 运行Docker容器
您在上一步中运行的hello-world容器是在发出测试消息后运行和退出的容器的示例。 容器可以比这更有用,它们可以是交互式的。 毕竟,它们类似于虚拟机,只是更加资源友好。
举个例子,让我们使用Ubuntu的最新图像运行一个容器。 -i和-t开关的组合为您提供了对容器的交互式shell访问:
docker run -it ubuntu
您的命令提示符应该更改以反映您现在正在容器内工作的事实,并应采用以下形式:
Outputroot@d9b100f2f636:/#
请注意命令提示符中的容器ID。 在这个例子中,它是d9b100f2f636 。 稍后您需要该容器ID以在要删除容器时标识容器。
现在您可以在容器内运行任何命令。 例如,让我们更新容器内的包数据库。 您不需要使用sudo为任何命令添加前缀,因为您以root用户身份在容器内操作:
apt update
然后在其中安装任何应用程序。 我们安装Node.js:
apt install nodejs
这将从官方Ubuntu存储库中安装容器中的Node.js. 安装完成后,验证是否已安装Node.js:
node -v
您将看到终端中显示的版本号:
Outputv8.10.0
您在容器内进行的任何更改仅适用于该容器。
要退出容器,请在提示符下键入exit 。
让我们看看下一步管理我们系统上的容器。
第6步 - 管理Docker容器
使用Docker一段时间后,您的计算机上将有许多活动(运行)和非活动容器。 要查看活动的 ,请使用:
docker ps
您将看到类似于以下内容的输出:
OutputCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED
在本教程中,您启动了两个容器; 一个来自hello-world图像,另一个来自ubuntu图像。 两个容器都不再运行,但它们仍然存在于您的系统上。
要查看所有容器 - 活动和非活动,请使用-a开关运行docker ps :
docker ps -a
您将看到类似于此的输出:
d9b100f2f636 ubuntu "/bin/bash" About an hour ago Exited (0) 8 minutes ago sharp_volhard
01c950718166 hello-world "/hello" About an hour ago Exited (0) About an hour ago festive_williams
要查看您创建的最新容器,请将-l开关传递给它:
docker ps -l
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
d9b100f2f636 ubuntu "/bin/bash" About an hour ago Exited (0) 10 minutes ago sharp_volhard
要启动已停止的容器,请使用docker start ,然后使用容器ID或容器名称。 让我们启动ID为d9b100f2f636的基于Ubuntu的容器:
docker start d9b100f2f636
容器将启动,您可以使用docker ps查看其状态:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
d9b100f2f636 ubuntu "/bin/bash" About an hour ago Up 8 seconds sharp_volhard
要停止正在运行的容器,请使用docker stop ,然后使用容器ID或名称。 这一次,我们将使用Docker分配容器的名称,即sharp_volhard :
docker stop sharp_volhard
一旦您决定不再需要容器,请使用docker rm命令将其删除,再次使用容器ID或名称。 使用docker ps -a命令查找与hello-world映像关联的容器的容器ID或名称,然后将其删除。
docker rm festive_williams
您可以使用--name开关启动一个新容器并为其命名。 您还可以使用--rm开关创建一个在停止时自行删除的容器。 有关这些选项和其他选项的更多信息,请参阅docker run help命令。
容器可以转换为可用于构建新容器的映像。 让我们来看看它是如何工作的。
第7步 - 将容器中的更改提交到Docker镜像
当您启动Docker镜像时,您可以像使用虚拟机一样创建,修改和删除文件。 您所做的更改仅适用于该容器。 您可以启动和停止它,但是一旦使用docker rm命令销毁它,更改将docker rm丢失。
本节介绍如何将容器的状态保存为新的Docker镜像。
在Ubuntu容器中安装Node.js后,您现在有一个运行图像的容器,但容器与您用来创建它的图像不同。 但是您可能希望稍后重新使用此Node.js容器作为新映像的基础。
然后使用以下命令将更改提交到新的Docker镜像实例。
docker commit -m "What you did to the image" -a "Author Name" container_id repository/new_image_name
-m开关用于提交消息,帮助您和其他人知道您所做的更改,而-a用于指定作者。 在启动交互式Docker会话时, container_id是您在本教程前面提到的那个。 除非您在Docker Hub上创建了其他存储库,否则存储repository通常是您的Docker Hub用户名。
例如,对于用户sammy ,容器ID为d9b100f2f636 ,命令为:
docker commit -m "added Node.js" -a "sammy" d9b100f2f636 sammy/ubuntu-nodejs
提交图像时,新图像将保存在您的计算机本地。 在本教程的后面,您将学习如何将映像推送到Docker Hub之类的Docker注册表,以便其他人可以访问它。
再次列出Docker图像将显示新图像以及从中派生的旧图像:
docker images
你会看到这样的输出:
OutputREPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
sammy/ubuntu-nodejs latest 7c1f35226ca6 7 seconds ago 179MB
ubuntu latest 113a43faa138 4 weeks ago 81.2MB
hello-world latest e38bc07ac18e 2 months ago 1.85kB
在此示例中, ubuntu-nodejs是新映像,它是从Docker Hub中的现有ubuntu映像派生的。 尺寸差异反映了所做的变化。 在此示例中,更改是NodeJS已安装。 因此,下次需要使用预先安装了NodeJS的Ubuntu运行容器时,您可以使用新映像。
您还可以从Dockerfile构建映像,这样您就可以在新映像中自动安装软件。 但是,这超出了本教程的范围。
现在让我们与他人分享新图像,以便他们可以从中创建容器。
第8步 - 将Docker镜像推送到Docker存储库
从现有映像创建新映像之后的下一个逻辑步骤是与您选择的几个朋友,Docker Hub上的整个世界或您可以访问的其他Docker注册表共享它。 要将映像推送到Docker Hub或任何其他Docker注册表,您必须在那里拥有一个帐户。
本节介绍如何将Docker镜像推送到Docker Hub。 要了解如何创建自己的私有Docker注册表,请查看如何在Ubuntu 14.04上设置私有Docker注册表 。
要推送图像,请先登录Docker Hub。
docker login -u docker-registry-username
系统将提示您使用Docker Hub密码进行身份验证。 如果您指定了正确的密码,则身份验证应该成功。 然后你可以使用以下方法推送自己的图像
docker push docker-registry-username/docker-image-name
要将ubuntu-nodejs映像推送到sammy存储库,命令将是:
docker push sammy/ubuntu-nodejs
上传图像时,该过程可能需要一些时间才能完成,但完成后,输出将如下所示:
OutputThe push refers to a repository [docker.io/sammy/ubuntu-nodejs]
e3fbbfb44187: Pushed
5f70bf18a086: Pushed
a3b5c80a4eba: Pushed
7f18b442972b: Pushed
3ce512daaf78: Pushed
7aae4540b42d: Pushed
...
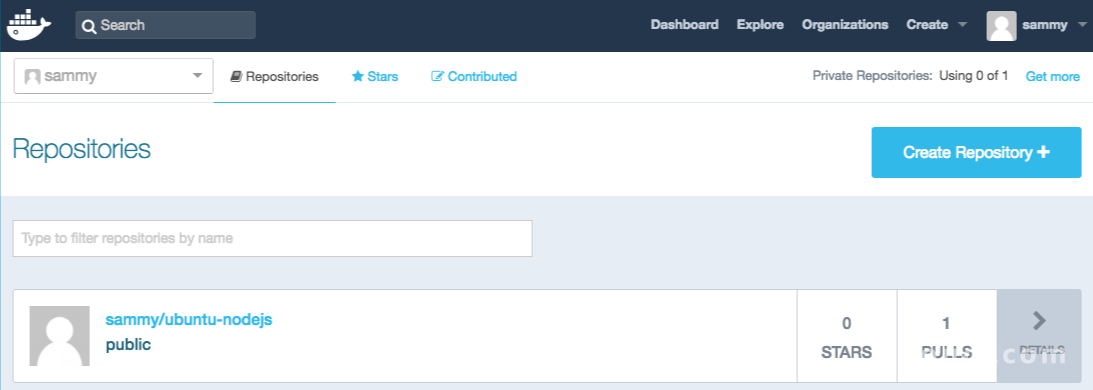
将图像推送到注册表后,它应该列在您帐户的仪表板上,如下图所示。
如果推送尝试导致此类错误,那么您可能没有登录:
OutputThe push refers to a repository [docker.io/sammy/ubuntu-nodejs]
e3fbbfb44187: Preparing
5f70bf18a086: Preparing
a3b5c80a4eba: Preparing
7f18b442972b: Preparing
3ce512daaf78: Preparing
7aae4540b42d: Waiting
unauthorized: authentication required
使用docker login并重复推送尝试。 然后验证它是否存在于Docker Hub存储库页面上。
您现在可以使用docker pull sammy /ubuntu-node<^>将图像拉到新计算机并使用它来运行新容器。
结论
在本教程中,您安装了Docker,使用了图像和容器,并将修改后的图像推送到Docker Hub。 现在您已了解基础知识,请浏览DigitalOcean社区中的其他Docker教程 。








